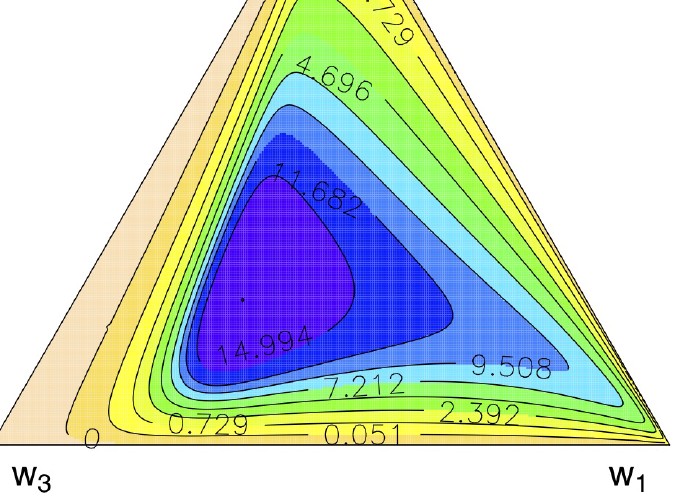
Figure 2
Abstract
The skew-normal and related families are flexible and asymmetric parametric models suitable for modelling a diverse range of systems. We show that the multivariate maximum of a high-dimensional extended skew-normal random sample has asymptotically independent components and derive the speed of convergence of the joint tail. To describe the possible dependence among the components of the multivariate maximum, we show that under appropriate conditions an approximate multivariate extreme-value distribution that leads to a rich dependence structure can be derived.
Type
Publication
In Statistics and Probability Letters